-

SEI NATO TRA IL 1969 E IL 1989?Aderisci allo screening gratuito per l’Epatite C, basta un semplice prelievo di sangue!
Quando l’infezione è ancora asintomatica può essere curata. -
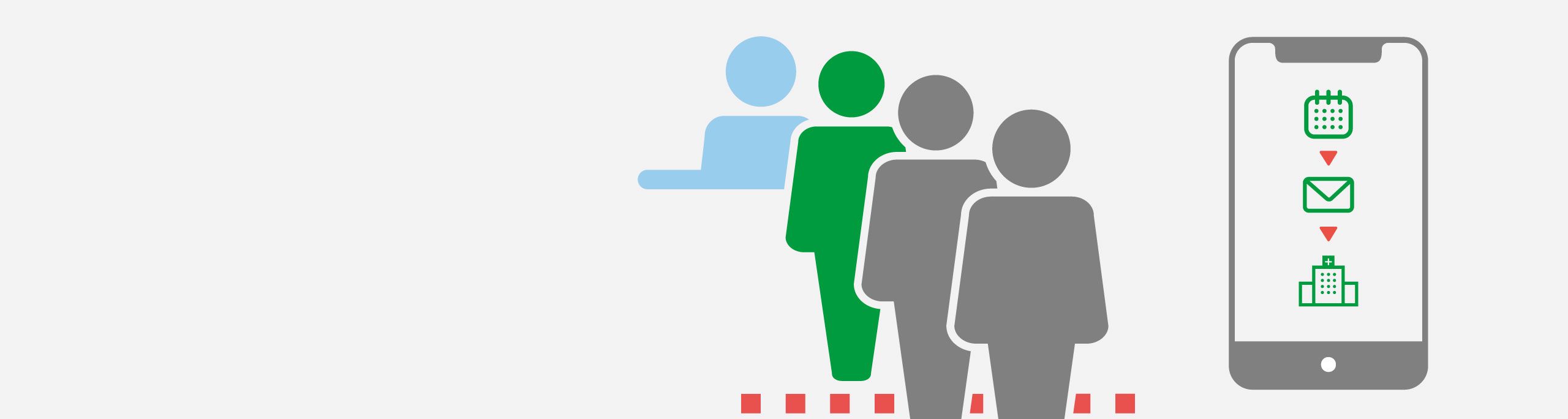
ESAMI DEL SANGUE?
PRENOTA IL TUO POSTO CON LO SMARTPHONECon ZeroCoda puoi prenotare il tuo accesso ai nostri Punti Prelievo
utilizzando un sito dedicato. -
MULTIMEDICA A CASA TUA
Il servizio infermieristico domiciliare che hai sempre cercato!
Prelievi, esami, terapie, medicazioni e assistenza con la stessa qualità, sicurezza, privacy e tempistica di refertazione dell’ospedale, senza doverti muovere da casa tua. -
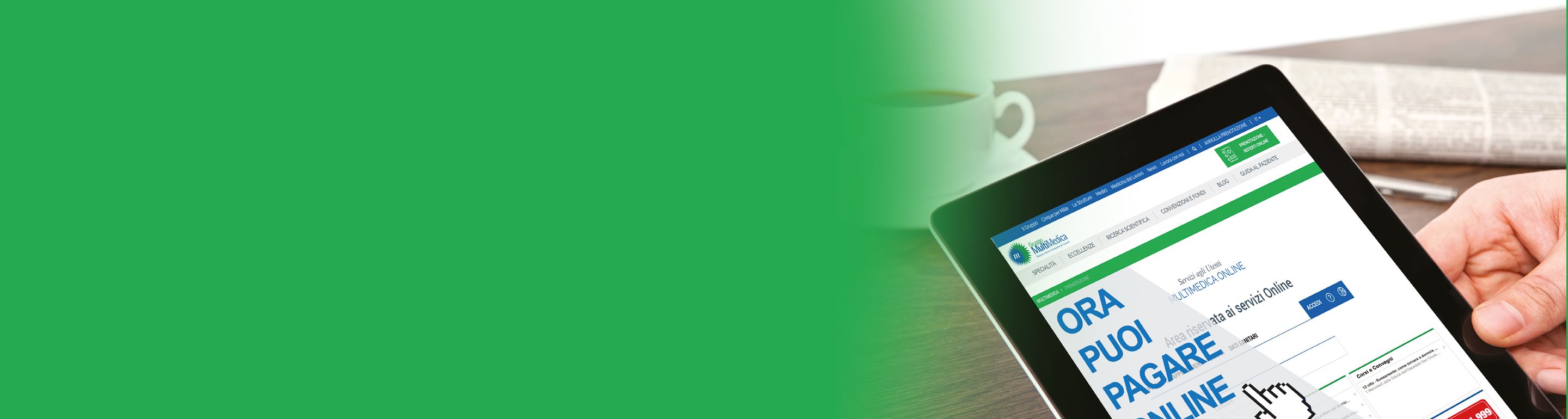
PRENOTAZIONE, PAGAMENTO E REFERTO
QUANDO VUOI, DOVE VUOI… BASTA UN CLICKÈ possibile effettuare il pagamento delle prestazioni sanitarie, prenotare e scaricare i referti direttamente dall’AREA RISERVATA del nostro portale.
La procedura è facile, intuitiva e sicura!

Gruppo MultiMedica
MultiMedica è una realtà sanitaria d’eccellenza nel panorama italiano, ed è il quarto gruppo privato accreditato in Lombardia. Fondata nel 1986, oggi è costituita da 8 strutture: ospedali ad alta specializzazione, poliambulatori specialistici e centri di ricerca scientifica che operano in sinergia integrando l’assistenza clinica alla ricerca e alla formazione universitaria per offrire a tutti le cure migliori.
MultiMedica è un punto di riferimento riconosciuto a livello nazionale per la cura e la riabilitazione di malattie cardiovascolari, pneumologiche e neurologiche, la diabetologia, l’oculistica pediatrica, l’area materno-infantile, la chirurgia della mano, la senologia.
Con un team di 3000 persone tra personale sanitario, tecnico e amministrativo, MultiMedica garantisce ogni anno oltre 4 milioni di prestazioni ambulatoriali, 25.000 interventi chirurgici, e 33.000 accessi al Pronto Soccorso.
Al centro dell’attività di MultiMedica c’è sempre il paziente, con i suoi bisogni fisici, psichici, emotivi e socio-relazionali. L’innovazione scientifica, le più avanzate apparecchiature tecnologiche e la competenza professionale sono solo strumenti al servizio del paziente.
La mission di MultiMedica è migliorare la salute e il benessere della popolazione, creando percorsi di assistenza e cura innovativi e personalizzati, e promuovendo una rete di clinica, ricerca e formazione inclusiva, aperta al territorio, ai medici, alle famiglie e alle istituzioni.

Servizi Online
Approfitta della comodità dei servizi online per prenotare 24 ore su 24, scaricare i tuoi referti, saltare la coda per il tuo prelievo e molto altro!
Ospedali, poliambulatori, centri di ricerca
In evidenza
Tanti specialisti, un’unica missione
In MultiMedica operano oltre 2000 tra medici e professionisti sanitari altamente qualificati per offrirti la miglior cura e assistenza possibile.
La nostra missione consiste nell’affiancarti e nel supportarti nel percorso terapeutico più adatto, attraverso un approccio multidisciplinare e l’erogazione di servizi di qualità personalizzati sulle singole esigenze.
Wiki MultiMedica
In questa sezione puoi approfondire una vasta gamma di patologie che trattiamo nei nostri ospedali.
Scopri come MultiMedica può essere al tuo fianco per affrontare le tue esigenze di salute in modo completo e affidabile, a partire dalla corretta informazione medico-scientifica.
Scopri il centro più vicino a te
I.R.C.C.S. MultiMedica
Ospedale San Giuseppe
Ospedale MultiMedica Castellanza
Ospedale MultiMedica Limbiate
PST-Polo Scientifico e Tecnologico MultiMedica
MultiMedica Cadaver Laboratory
MultiLab – Centro MultiMedica di Medicina di Laboratorio e Anatomia Patologica
Centro Dialisi del Pio Albergo Trivulzio
Ambulatorio Multispecialistico MultiMedica
- 02 86878889 (Servizio Sanitario Nazionale)
- 02 99961999 (Privati, Fondi e Assicurazioni)
Consulta gli orari di apertura delle sedi: clicca qui.
Dicono di noi
Leggi le storie dei nostri pazienti, gli articoli sulla stampa che parlano di noi, e rimani aggiornato sulle novità!